Overview
CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin are often used together in longevity and performance circles. CJC-1295 is a modified GHRH analog that prolongs growth hormone release; Ipamorelin is a growth hormone secretagogue (GHSR agonist) that stimulates GH with relatively selective action. Together, they are marketed for enhanced GH output, anti-aging, and recovery. Regulatory status is complex: both peptides individually have been on the FDA’s Category 2 list, and nominations were withdrawn in September 2024—they are not on the Category 1 (compoundable) list. The FDA has also flagged CJC-1295 for cardiac side effects. Patients and providers must understand that obtaining these compounds through US compounding may not be legally supported and that safety concerns exist.
People seek this combination for the same reasons they seek other GH-supporting peptides: improved body composition, sleep, recovery, and energy. It is important to weigh these goals against the current regulatory and safety landscape and to consider legal alternatives such as sermorelin where appropriate.
How It Works (Mechanism of Action)
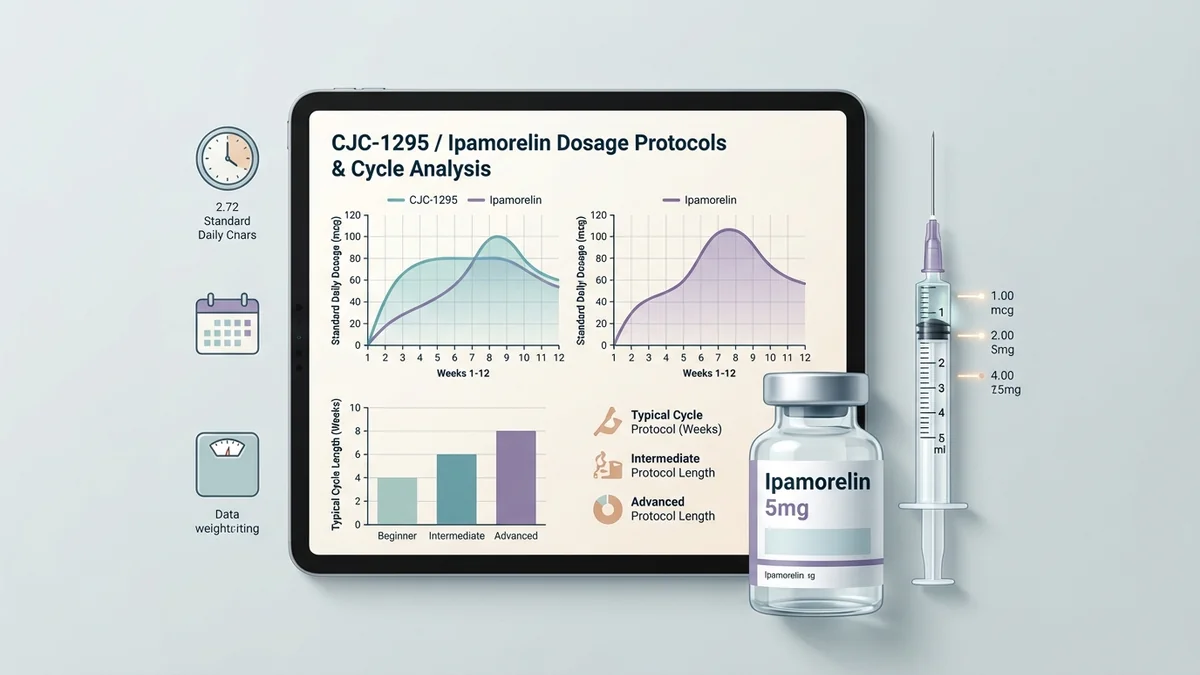
CJC-1295 is a modified GRF (1-29) analog with a longer half-life, leading to sustained GH release. Ipamorelin is a that stimulates the pituitary to release GH with minimal effect on other hormones (e.g., cortisol, prolactin). Used together, the intent is to produce a stronger, more sustained GH response than either alone. Evidence for synergy in humans is limited.