Key Takeaways
- TB-500 Fragment (17-23) is not FDA-approved and is available for research purposes only.
- Typical dosing protocols are derived from preclinical studies, with no standardized human dosing.
- Titration schedules are crucial for assessing tolerability and potential efficacy.
- Administration is typically via subcutaneous injection, requiring careful handling and storage.
- Medical supervision is essential to ensure safe and effective use in research settings.
What Is TB-500 Fragment (17-23)?
TB-500 Fragment (17-23) is a research peptide derived from the actin-binding region of Thymosin Beta-4. It is primarily investigated for its potential roles in wound repair, tissue remodeling, and regenerative signaling. For more detailed information, refer to the full profile.
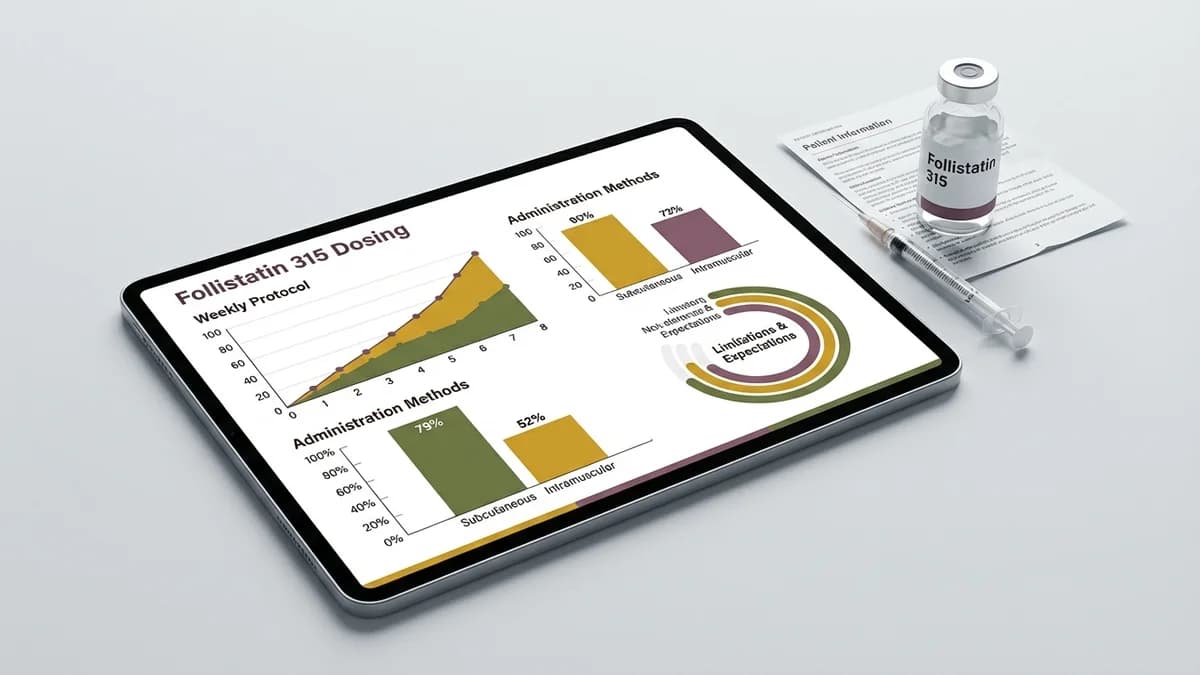
Standard Dosing Protocols
Currently, TB-500 Fragment (17-23) does not have an FDA-approved dosing protocol, as it is designated for research use only. In preclinical settings, dosing is often guided by animal studies and in-vitro experiments. For example, the synthesis and characterization of this peptide have been documented in research focused on its potential as a doping agent (PMID 22962027). Researchers typically use a range of microgram to milligram doses per kilogram of body weight, based on experimental objectives.
Titration Schedules
In research contexts, titration schedules are vital for determining the peptide's tolerability and efficacy. Initial doses are often conservative, gradually increasing based on observed effects and side effects. This careful escalation helps in minimizing adverse reactions and optimizing the peptide's potential benefits.
Administration Method
TB-500 Fragment (17-23) is usually administered via subcutaneous injection. This method involves injecting the peptide into the fatty tissue beneath the skin, often rotating sites to prevent irritation. Common injection sites include the abdomen, thigh, and upper arm. Proper storage, typically refrigerated, and reconstitution with bacteriostatic water are necessary to maintain peptide stability.
Factors That Affect Dosing
Several factors can influence the dosing of TB-500 Fragment (17-23) in research settings. These include the subject's body weight, specific research goals, concurrent medications, and overall health status, particularly liver and kidney function. Researchers must adjust dosing accordingly to accommodate these variables.
What Happens If You Miss a Dose
In a research setting, missing a dose of TB-500 Fragment (17-23) could affect study outcomes. While specific guidance is limited, researchers generally recommend administering the missed dose as soon as possible, unless it is close to the time of the next scheduled dose. Consistency is crucial for maintaining study integrity.
Dosing Compared to Similar Peptides
When compared to other peptides like BPC-157, TB-500 Fragment (17-23) may require different dosing strategies due to variations in molecular structure and mechanism of action. BPC-157, for instance, has been studied more extensively in human trials, providing a clearer dosing framework.
What the Evidence Does Not Show
The current research on TB-500 Fragment (17-23) is limited to preclinical studies. There is a lack of long-term safety data and standardized dosing protocols for human use. The peptide's effects in humans remain largely theoretical, emphasizing the need for further research.
FAQ
Q: Is TB-500 Fragment (17-23) safe for human use?
A: TB-500 Fragment (17-23) is not approved for human use and is available only for research purposes.
Q: How should TB-500 Fragment (17-23) be stored?
A: It should be stored in a refrigerator and reconstituted with bacteriostatic water to maintain stability.
Q: Can TB-500 Fragment (17-23) be used in combination with other peptides?
A: While some research may explore combinations, any concurrent use should be under strict research protocols due to the lack of comprehensive human data.
Q: What is the typical administration route for TB-500 Fragment (17-23)?
A: The peptide is typically administered via subcutaneous injection.
Q: How does TB-500 Fragment (17-23) compare to TB-500?
A: TB-500 Fragment (17-23) is a specific segment of the larger TB-500 molecule, focusing on specific actin-binding properties.
Medical Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider before starting any treatment.
Find a Peptide Therapy Clinic Near You
Browse our directory of verified peptide therapy clinics across the United States. Compare providers, read reviews, and request a consultation.
PeptideClinicLocator.com does not provide medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before starting any peptide therapy. Regulatory status may change.